Many changes in the legs on the legs can make people think of having a fungal nail infection, from a medical point of view, known as onychomycosis. The fungal infection of the nails sometimes makes the condition contagious or is associated with poor hygiene. In fact, up to 10% of all adults have fungal nail infections. This percentage increases to 20% of adults aged 60 or over 60 years. In fact, the nails not by appearance normally can be caused by a series of conditions, including fungal infection, but not limited. There are many other reasons why nails may seem different.
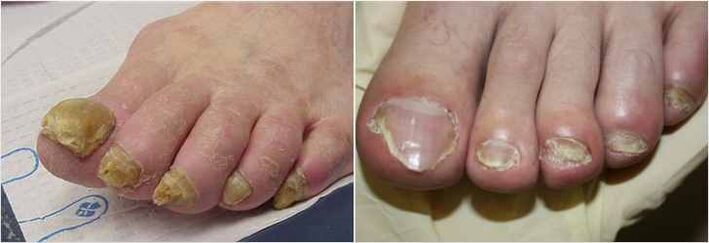
Treatment of the nail fungus
Onychomycosis is a fungal infection, usually caused by a special type of mushrooms, known as dermatophyte. Since most of these infections are relatively superficial, it would seem that current procedures should work well. This is not the case, because the nail is relatively impenetrable. Examples of states that are often exchanged for fungal nails include yellow (onicolisi), hematoma, green nails (caused by pseudomonas bacteria), bones (usually associated with psoriasis), nail infection (steamonichia) and late lesions.
What other conditions can be undertaken for fungal nails?
Here are some other conditions that can be instead of fungal nails:
Lines and crests: they are common and can be considered normal. They can worsen during pregnancy. A large groove in the center of the nail can be caused by injuries. Some people may notice these changes after chemotherapy.
Senile nails: with age, the nails become fragile and develop the crests and the separation of the layers of nails at the end of the nail. To avoid this, it is necessary to use special solutions and bathrooms.
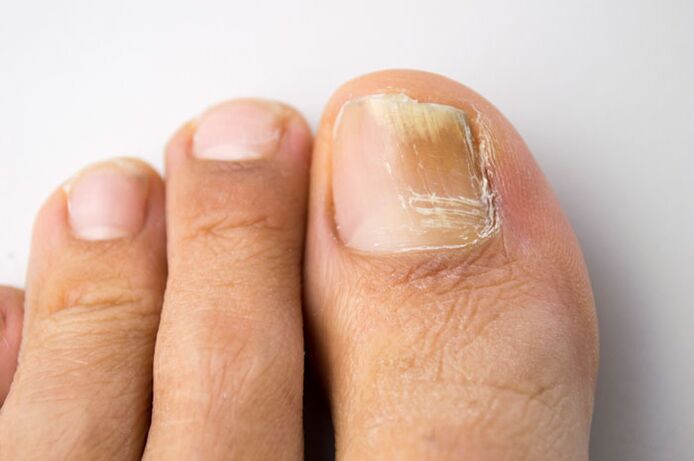
White or yellowish nails can occur due to onicolisi. This means separating the dish from the nail base. The color that the shape is the air under the nail. The treatment consists in briefly cutting the plate, not to clean under it and polish. If you need to hide the color, you have to wait for two to three months. Constant onkelos can make nails susceptible to fungal infections. The red or black plates due to the hematoma or blood under the nail, as a rule, occur for injuries. If there is a black stain under the nail, which is not caused by injuries, it is necessary to visit a dermatologist or an orthopedist to make sure this is not melanoma (the type of skin carcinoma associated with pigmented cell). Simple biopsy can exclude malignancy (cancer).
The green plates can be caused by pseudomonas bacteria, which grow under the nail, which is partially separated from the nail base. This infection can cause an unpleasant smell of nails. The treatment consists in briefly cutting the nails every four weeks, do not clean, polish if it is necessary to hide the color and wait for two to three months. It is also advisable to avoid immersing the plates in any water (and drying the legs in the bottom after the bath. If the problem has not disappeared, there are prescriptions of drugs for the treatment that the doctor prescribes. Even the nails affected by psoriasis can be brown.
The edema and the redness of the skin around the nail are called speaking. This is an infection of the skin on the bottom of the nail (cuticle). If the infection is acute (it has a quick start), it is usually caused by bacteria. It can react to the hot baths, but it is better not self -produce, but see a doctor immediately. Chronic parrony occurs when the cuticle is inflamed or irritated over time. Sometimes mushrooms use damaged skin and infect it. Therapy begins with the fact that the skin remains dry and excreted by the water. If the problem does not disappear, you need to consult a doctor. Antibiotics are often not used, but they can be requested with a serious infection.
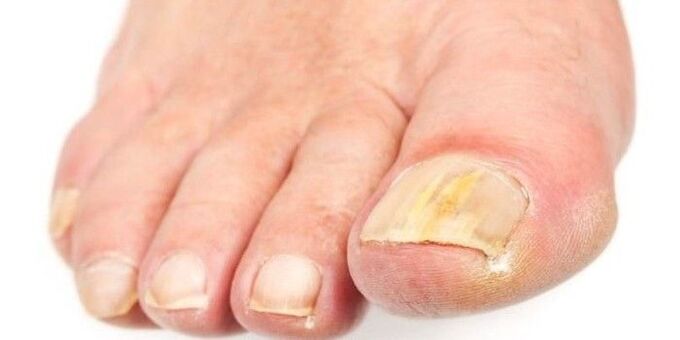
Chronic nails lesions can cause damage to the nails, which can look a lot about fungal nails. Some lesions can cause constant changes that can imitate the appearance of fungal nails. Microconidii Trichophophyton mushroom, which lives in the ground and can lead to fungal skin infections, hair or nails.
What does fungal infections cause and what are some risk factors?
In healthy healthy people, fungal nail infections are often caused by a mushroom, which falls into wetlands. Common types, such as in the gym or swimming pools, common sources. The transition to the nails that use an inadequate cleaning of tools (for example, clipper, fillets and toilet toilets) in addition to life with family members who have fungal diseases, are also risk factors. It has been shown that athletes are more susceptible to the nail fungus.
It is assumed that this is due to the fact that the densely narrow and sweaty boots associated with the repeated injury of the nails on the legs. The presence of sporting loads makes the mushroom more likely infected the nails on the legs. The repeated injury also weakens the plate, which makes it more susceptible to fungal infections. These include everything that worsens the immune system can make a person prone to the infection from a mushroom. These include conditions such as AIDS, diabetes, cancer, psoriasis or adoption of any immunosuppressants, such as steroids.
Are fungal nails contagious?
Although the mushroom should be obtained somewhere, it is not very contagious. It is so common that finding more than one person in a family who has this is nothing more than an accidental coincidence. The mushroom can be transmitted from person to person, but only with constant intimate contact.
What are the fungal symptoms and nail signs?
Although fungal nails are generally cosmetic problems, some patients experience pain and discomfort. These symptoms can be aggravated by shoes, activities and finishes for improper nails. There are many types of mushrooms that can influence nails. However, the most common, however, is called Trichophophyton Rubrum. This type of mushroom tends to infect the skin (known as dermatophyte) and manifests itself in the following specific methods. Start at the ends of the nails and raises the plate: it's called "distal onychomycosis". This is the most common type of nail fungal infection in adults and children (90% of cases).
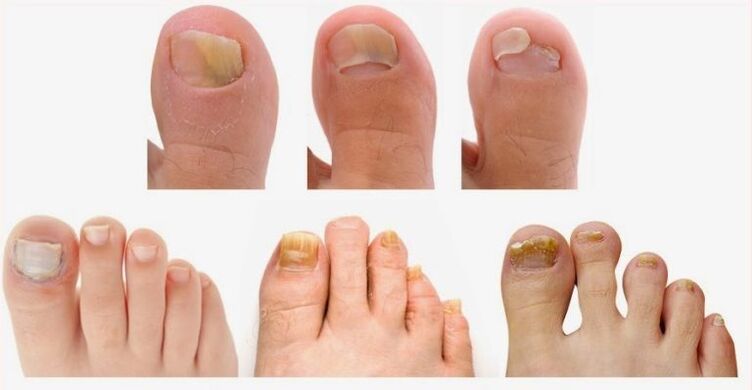
It is more common in the fingers of the feet, the thumb is usually the first to influence. The risk factors include elderly age, swimming, sports loads, psoriasis, diabetes, family members with infection or a depressed immune system. Usually it starts as an colorless area at the inches of the thumb and slowly spreads to the cuticle. It is often accompanied by Onolisi. The most common cause is T.
Start at the base of the nail and increases a nail: it is called "onychomycosis of the proximal tendon". This is the least common type of fungal damage (about 3% of cases). It looks like a distal guy, but begins with a cuticle (base of the nail) and slowly spreads on the tip of the nail. This type is almost always found in people with a damaged immune system. It is rarely possible to see fragments under the tip of the nail with this condition, unlike the distal onychomicosis. The most common cause is the T. Rubrum mold and the dermatophyte.
Onychomicosis of the yeast: this type is caused by a yeast called Candida and not by the Trichophyton mushroom, called above. This is more common in nails and is a common cause of fungal nails. Patients can be associated with paronial (cuticle infection). Candida can cause yellow, brown, white or inspected nails. Some people who have this infection also have mushrooms in their mouths or chronic parronia), which is also infected by the pores. Onychomicosis of the white surface: in this state of a nail, a doctor can often clean the white powder material at the top of the nail plate. This condition is more common in tropical environments and caused by a well -known mushroom and management of trihofitii.
What tests are used by health specialists to diagnose fungal nails?
It has been shown that only a physical examination is an unreliable method to diagnose fungal nails. There are many conditions that can make the nails look damaged, so doctors also have a difficult time. In fact, studies have shown that only about 50% - 60% of the abnormal cases of the nails were caused by a mushroom. Therefore, laboratory tests are almost always indicated. Some insurance companies may even ask for a confirmation of a laboratory test for diagnostics to cover an antifungal medicine. A sampling plate is obtained by cutting the nail or by piercing a hole. This piece is sent to the laboratory in which it can be painted, grown or tested using the PCR (to identify the genetic material of the organisms) to identify the presence of the mushroom.
If the negative result of the biopsy is accompanied by a high clinical suspicion, for example the frayed, bleached, inspected and loose plates, this requires a second test due to the prevalence of false negative results in these tests. Most of the drugs used to treat nails mushrooms have side effects, so you should know the contraindications.
Which specialists treat the nail fungus?
There are several doctors who can provide a nail fungus treatment. The attending physician, the dermatologist or the orthopedist can treat the nail fungus. Each of these doctors can provide adequate diagnosis and prescribe specific drugs for a fungal infection. An orthopedic or dermatologist can shake the upper layer of the nail or even remove part of the nail.
What treatment of fungal nails is required?
Cremes and other pertinent drugs are traditionally less effective against the nail fungus than oral medicines. This is due to the fact that the nails are too complicated for the penetration of external applications. It is also difficult to adhere to local treatment patterns. Often these drugs require daily applications during the period of time up to a year to see the results. One of the main advantages of local treatment is the minimum risk of serious side effects and the interaction with drugs compared to oral therapy.
Coralline antifungal therapy operates in about 50-75% of cases, depending on the drug. This can take from nine to twelve months to make sure it works or not, because how long it is necessary to build the nail. Even when the therapy works, the mushroom can return to about 20-50% of cases. Currently, oral antifungal therapy is considered the best tool for the treatment of mushrooms on the legs due to higher healing rates and a shorter duration of the treatment than local therapy.
There are several innovative treatment methods that are still controlled:
- Laser therapy or photodynamic therapy use the use of active light agents on a plate, followed by a brilliant light of the corresponding wavelength on the nail.
- The use of electric current to help the absorption of relevant antifungal drugs in a nail: it is also called Ionofori.
- The use of a special nail polish that changes the microclimate for nails to make it inhospitable for the growth of the mushroom: if it works, it can be an economic way to treat this problem in the future.
A way to finally get rid of the nail fungus is the operation. Onhomicosis surgical treatment includes the removal of nails. However, this often provides only temporary relief and the impact is common if further antifungal drugs (oral or local) are not used simultaneously. However, surgical removal can be justified if the touched nail is associated with other factors such as injuries or infections.
Is it possible to prevent the appearance of the nail fungus on the legs?
Since the mushroom really thrives in hot wet areas (for example sweaty legs), there are some areas that should be avoided or used with caution. It is assumed that showers, changing rooms and swimming pools are sources of mushrooms, although there are no studies that confirm this fact.
The paint and acrylic nails also make a less "breathing" dish and make it more susceptible to fungal infections. Mushrooms are everywhere - in the air, dust and ground. Hygienic measures, such as spraying socks and shoes, are reasonable and perhaps these measures can even help a little. However, avoiding dense boots, not that they breathe for sports facilities, it could prove to be the best prevention. Daily washing of the legs and drying between the fingers can help prevent the nail fungus. Mushrooms are transferred to pets, such as cats and dogs. However, they often don't cause a disease.
How to determine the nail fungus?
The treatment of fungal nails can be difficult and can take up to 18 months. Reinfection and reinfection are common (refection frequency of 40% -70%). An attempt to remove or modify the risk factors, if possible, is important to prevent the re -infection. People who have medical diseases predisposing them to fungal lesions can be treated even longer by the mushroom.
Tips for prevention of the treatment of the nail fungus
The mushroom causes only 50% -60% of the nails not normally inflated. It is difficult to immediately notice the difference between the various reasons for the bleached nails (also for doctors). Onychomycosis is often not treated. The reasons why medical treatment is needed mainly with lesions of the skin of the legs or nails.
























